

This platform is an effort to find the key drivers, challenges and opportunities for the solid waste management market and how that can be used to handle waste management issues in India. This is an online platform to sell & buy waste by anyone and act as Flipkart or Amazon for Waste produced in the country. This platform makes effort to bring all the players in waste management system under single roof and act as aggregator bridging the gap between demand and supply of the recyclable waste, helping the government entities to show case the available recyclables with them through online to attract the potential buyers





This platform act as a trading portal where buyers can bid from corporation and other players
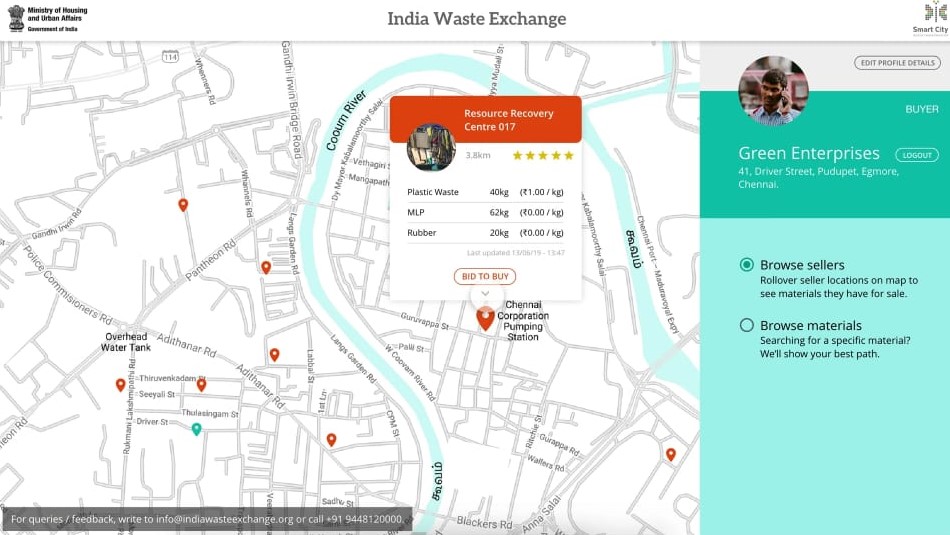
Acts as a portal to showcase & market the segregated waste available, which brings more buyers
Easy to use Dashboard
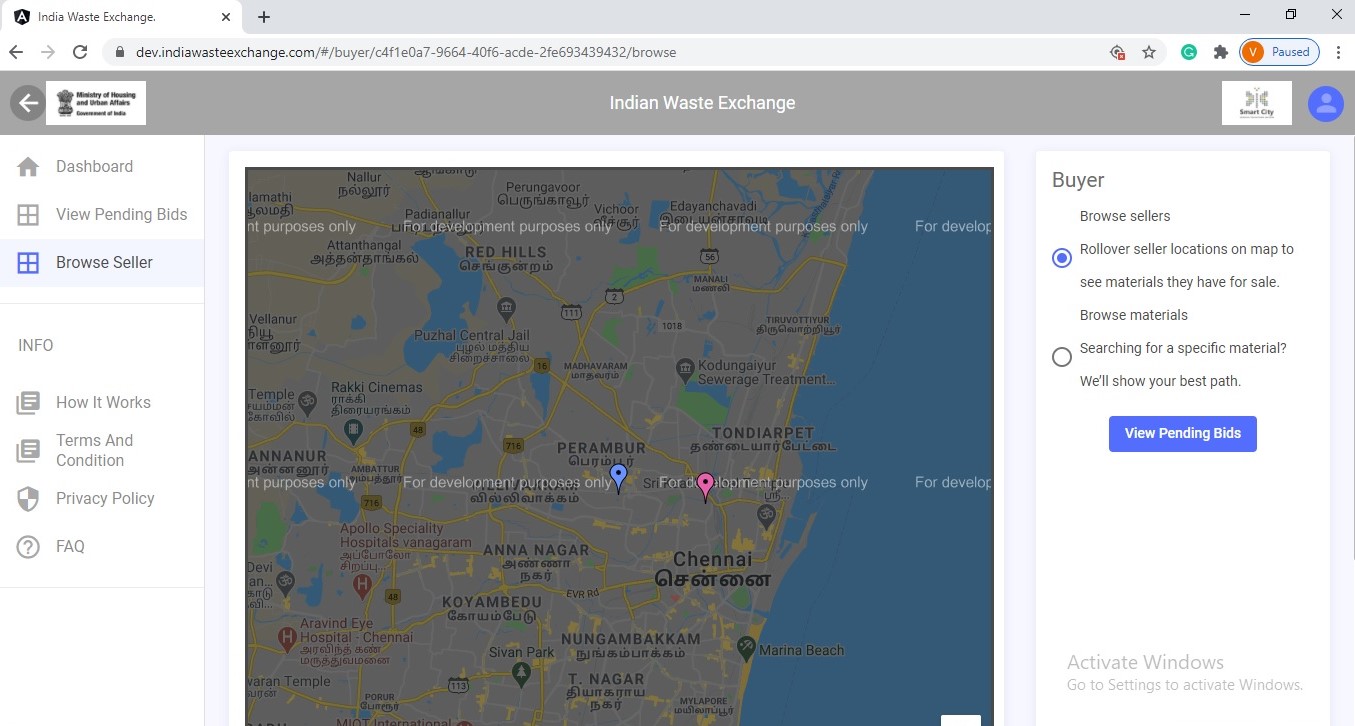
GIS Mapping for purchase

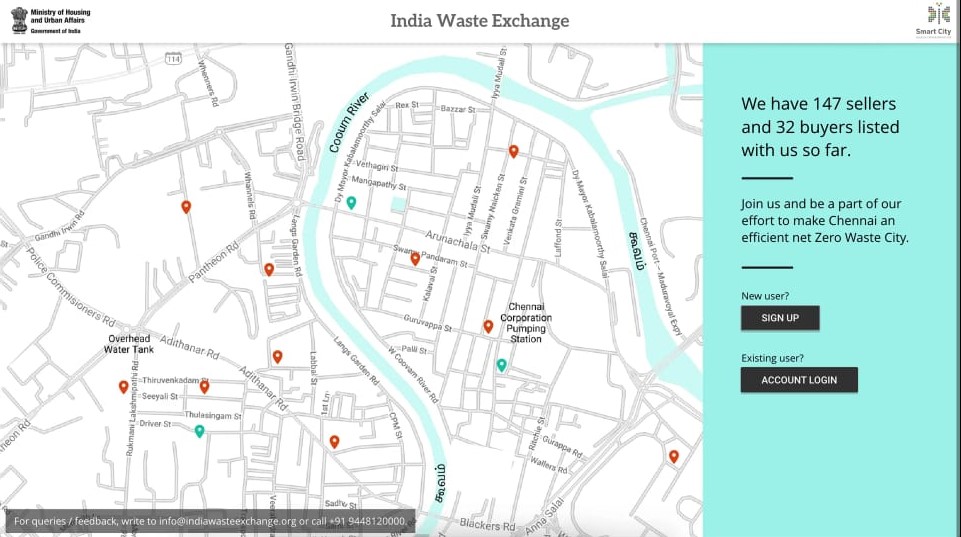
Launched in Chennai and it is in live for the past 11 months wherein which over a period of 6 months 700T waste sold through this platform with 3 lakh revenue increased for corporation through this platform encouraging 1,000 numbers of buyers register.
Waste management is an ongoing challenge due to weak institutions, chronic under-resourcing and rapid urbanization. Legislation for city level comprehensive waste management plan is not available for many cities. Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) suffer from various issues like infrastructure and capacity constraints to address the multi-dimensional problems of waste management. Not much focus on secondary market and niche segment for strengthening of waste markets. Financial constraints of ULBs and lack of incentives to public is acting as barrier for segregation at source, which is a vital component of waste management. Business model or plan showcasing the potential of city to attract public and private investments is not available.
The Project tries finding the key drivers, challenges and opportunities for the global solid waste management market and how that can be used for waste produced in India. Also, Understanding how local solutions (Wards, Villages) and Private innovative solutions (Startup’s, NGO’s) in SWM can be scaled up to meet the waste management requirements across India.Finally Creating Framework to find Ways by which ULB’s can attract Public and Private Investments in waste management by having Exchange Portal for waste processing.
Literature review on various existing waste management practices and approach available across India and world with major focus on local successful initiatives (ULB’s, NGO) and innovative examples(Start up’s) was conducted during Phase 1. This was followed by preliminary discussions with ULBs and other identified stakeholders, sectoral experts and mentors on waste management.
This will then be followed by City Selection of 3 cities based on socio-economic, governance and other functional parameters (amount of waste generation and processing, leadership capacity of ULB, city’s urbanization growth, carbon footprint etc.)
Post city-selection, the city was studied completely for all the waste being produced and ways by which the waste is processed. After which effective ways to handle waste management was be devised and process will be established to link it with secondary markets to form a cyclic economy around this process. By integrating waste management of various kinds of waste and understanding the potential attached to it. This Model was piloted in one of the selected cities which is Chennai.
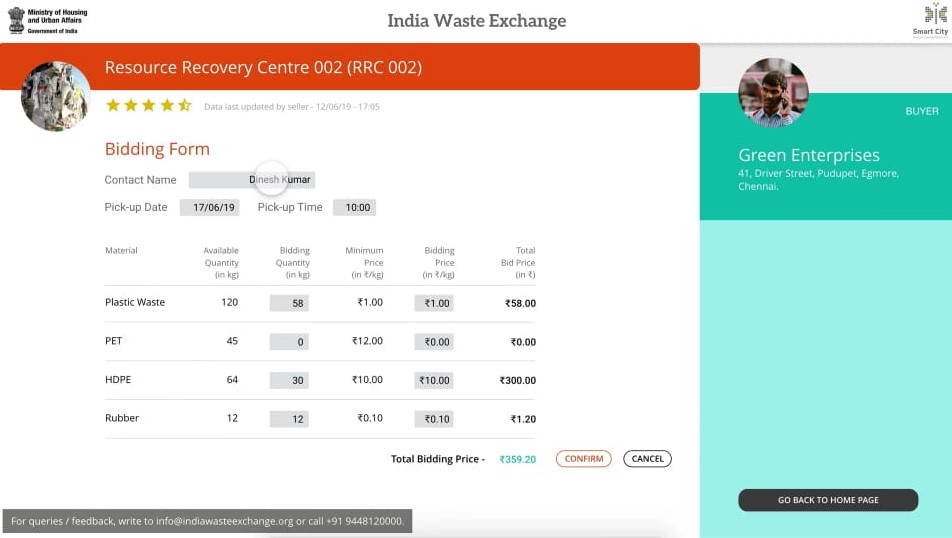
India Waste exchange is an online platform to sell and buy waste by anyone. It literally act as Flipkart or Amazon for Waste produced in the country.
India Waste Exchange makes effort to bring all the players in waste management system under single platform and act as aggregator. Waste exchange will try to bridge the gap between demand and supply of the recyclable waste. It will help government entities like corporation to show case the available recyclables with them online to attract the potential buyers.
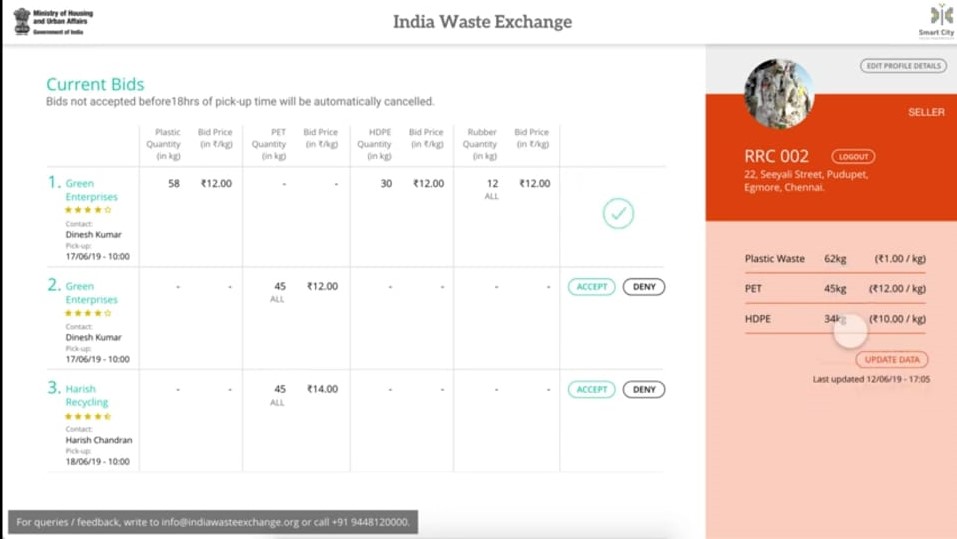
Waste Exchange in an online platform which works both on PC and Mobile. This platform will act as a trading portal where buyers can bid from corporation and other players. Since it is a trading portal, zero downtime of server ha to be maintained and also this platform uses map to identify potential sellers and their details.
To test this platform, initial pilot was done in Greater Chennai Corporation. The platform was called “Madras Waste Exchange”. It was launched in December ,2019 by GCC Commissioner G.Prakash I.A.S. In phase one of Madras Waste Exchange, Corporations RRC’c will be listed in the platform and in second phases, this waste exchange will be scaled up horizontally and vertically. It will absorb more players in the field and other kinds of waste like e-waste etc. The Platform attracted more than thousand buyers and four hundred sellers in three months. Further, GCC sold more than 700 tons of waste in three months. The Madras Waste Exchange helped Greater Chennai Corporation (GCC) in the following ways. a. It reduced the amount of garbage going to landfill. b. It acted as a portal to showcase and market the amount of segregated waste available with corporation, which can bring more buyers to approach corporation. c. Chennai become the first city in India to have waste exchange for municipal solid waste. d. E-Waste could be handled in better way since there is no clear mechanism as of now to collect and handle it. e. Repository of data on waste creation and processing will help in policy preparation process in future. Taking this as a Proof of Concept (POC), Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs along with Chennai Smart City Chennai (CSCL) has decided to scale the platform to National Level.