



 |
The impact of the coronavirus pandemic on gender equalityThe lockdowns triggered by COVID-19 are taking a disproportionate toll on women in the labour market, as the sectors with high rates of female employment are experiencing heavier job losses while increased childcare needs during school closures exert an outsized impact on working mothers. Still, this column finds reason to hope that by promoting flexible work arrangements and putting the childcare obligations of both genders into plain sight, the crisis may reduce labour-market barriers in the long run. Link to the article: https://voxeu.org/article/impact-coronavirus-pandemic-gender-equality
|
 |
Urbanization and humidity shape the intensity of influenza epidemics in U.S. citiesInfluenza epidemics vary in intensity from year to year, driven by climatic conditions and by viral antigenic evolution. However, important spatial variation remains unexplained. Here we show predictable differences in influenza incidence among cities, driven by population size and structure. Weekly incidence data from 603 cities in the United States reveal that epidemics in smaller cities are focused on shorter periods of the influenza season, whereas in larger cities, incidence is more diffuse. Base transmission potential estimated from city-level incidence data is positively correlated with population size and with spatiotemporal organization in population density, indicating a milder response to climate forcing in metropolises. |
 |
Development of an Assessment Method for Investigating the Impact of Climate and Urban Parameters in Confirmed Cases of COVID-19: A New Challenge in Sustainable DevelopmentSustainable development has been a controversial global topic, and as a complex concept in recent years, it plays a key role in creating a favorable future for societies. Meanwhile, there are several problems in the process of implementing this approach, like epidemic diseases. Hence, in this study, the impact of climate and urban factors on confirmed cases of COVID-19 (a new type of coronavirus) with the trend and multivariate linear regression (MLR) has been investigated to propose a more accurate prediction model. For this propose, some important climate parameters, including daily average temperature, relative humidity, and wind speed, in |
 |
Rapid Urban Health Security Assessment (RUHSA) ToolLocal governments and sub-national authorities are often the first to respond to public health emergencies, sometimes with wide-ranging responsibilities but often insufficient capacities to deal with them. The Rapid Urban Health Security Assessment (RUHSA) Tool is a resource designed primarily for local government leaders and policy makers to support public policy, decision making and organization as they prioritize, build, and implement capacities to improve local-level health security. |
 |
Why India has the upper hand against COVID-19India, currently under 21-day lockdown, is fighting back against COVID-19 with a “cluster containment strategy” to contain the disease within a defined geographic area by early detection of cases, breaking the chain of transmission and thus preventing its spread. As per a statement issued by the Indian Health Ministry, India will be following a strategic approach taking into account different possible scenarios – travel-related cases, local transmission of COVID-19, large outbreaks amenable to containment, and widespread community transmission of COVID-19. The World Health Organization on Tuesday praised India for its tough and timely efforts to control the spread of coronavirus. There has been |
 |
How cities around the world are handling COVID-19 - and why we need to measure their preparedness
|
 |
Covid-19 and Cities We WantImagine our lives as urban residents in the post-COVID19 world. Currently even as the administration at national, state, city and Gram Panchayat level is focused and engaged in responding to the COVID crises, we need to initiate a dialogue between the experts from various fields and contemplate will there be change in our city level functioning or will it revert to the business as usual approach once the normal operations of the city resume. A few years ago, many nations committed, “to foster healthy societies by promoting access to adequate, inclusive and quality public services...” through the implementation of The Agenda 2030-Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), the New Urban Agenda, the Paris agreement and the Sendai Framework. The global commitments and aspirations were well |
 |
Governments’ response to COVID-19: From pandemic crisis to a better futureThe rapid spread of the COVID-19 virus is challenging governments to act in ways normally reserved for war, depressions, and natural disasters. The pandemic has caused global upheaval that may endure for months—or longer. Governments are taking extreme measures to limit the human cost and economic disruption. It is the most consequential set of public policy and mass behavior change actions most of us have seen in our lifetimes. In a fast-moving crisis, as information swarms in from every direction, citizens look to their governments for information, guidance, and leadership. They expect to be kept safe and healthy. Pressure on public officials to act is enormous. How can they hope to gain clarity amid chaos? How can they move from ad |
 |
Potential impact of COVID-19 on the Indian sanitation ecosystemCOVID-19 has infected nearly 2.5 million people in more than 210 countries.2 Beyond the human tragedy, this pandemic has also ravaged the entire world economy. Human and economic cost is likely to be more significant for lower and middle-income countries, that generally have limited coverage and capacity of water supply and sanitation systems, lower healthcare capacity and larger informal sectors. This paper, prepared by KPMG in India and RTI, has been put together using insights from more than 25 interviews with senior sanitation sector experts. Key findings are as below:
|
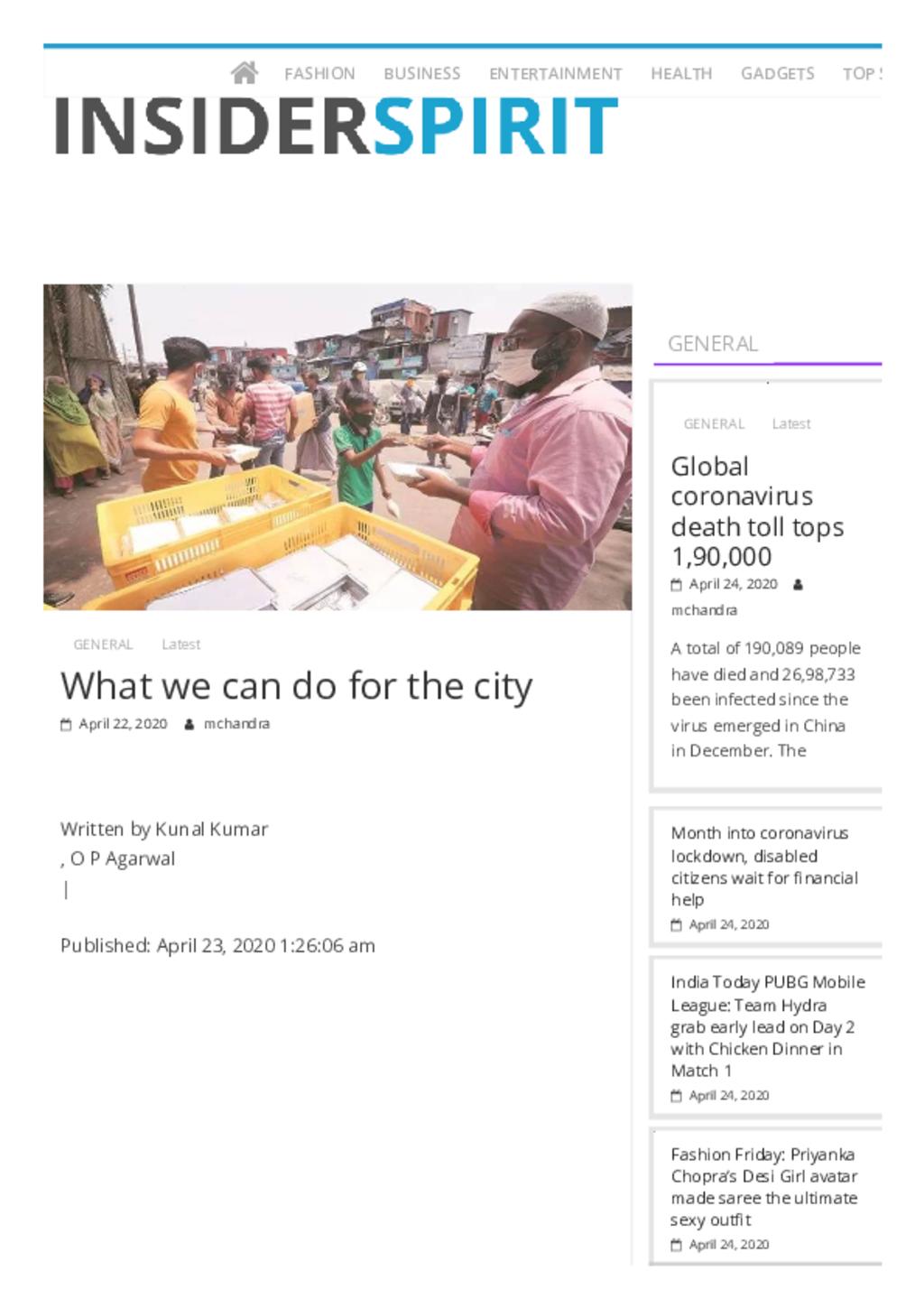 |
What Can We Do For The City: From using technology to track COVID-19 cases to setting up community kitchens, battle against pandemic has kindled innovation, ways to connectCOVID-19, a new disease of the coronavirus family, has engulfed almost the entire world. Developed countries such as the US, Spain, Italy, France and Germany seem to have suffered the most. India has managed to keep the number of those infected relatively low, despite |